What’s the difference between alkaline water and filtered water? Alkaline water has an elevated pH value of between 7-14. Filtered water is water that has been passed through a water filtration device to remove contaminants. They are two different types of water.
WHICH IS BETTER ALKALINE WATER OR FILTERED WATER?
Which type of water is better – alkaline water or filtered water? Alkaline water and filtered water are two completely different types of water.

Alkaline water has an elevated pH. This means it is the opposite of acidic water. Alkaline water is better if you want to increase the pH of your water and neutralize excess acidity levels.
Filtered water has been treated to remove contaminants and toxins. It is a way of cleaning water. It purifies water by passing it through a water filter and removing particles and chemicals.
If your drinking water is contaminated and needs to be purified – filtered water is better. By filtering contaminated water you can make it safe to drink.
WHAT IS ALKALINE WATER?
Alkaline water is any water that has a pH above 7. The pH scale is used to measure how acidic or alkaline a substance is. It runs from 0-14.

Anything below 7 is acidic, anything above 7 is alkaline, and 7 is neutral. The higher the value the more alkaline a substance is. Similarly, the lower the value, the more acidic a substance is.
Alkaline water has recently seen a surge in popularity. People claim that drinking alkaline water neutralizes excess acidity in the body and boosts health. However, there is no scientific evidence to support these claims. For more information on alkaline water – see here.
HOW TO MAKE ALKALINE WATER
How is alkaline water made? The best way to make alkaline water is to use an alkaline water ionizer machine. These home appliances use your regular tap water supply and convert it to alkaline water.

Other methods for making alkaline water at home include using pH drops, baking soda, lemon juice, vinegar, salt, coconut, and cucumber. For more information on how to make alkaline water at home – click here.
ADVANTAGES OF ALKALINE WATER
What are the advantages of alkaline water? Proponents of alkaline water say that drinking it comes with a whole range of health benefits. But, none of these claims are backed up by scientific evidence.
The potential benefits of alkaline water are better skin health, system detoxification, easing acid reflux, and reducing blood pressure. Although, medical professionals point out that there is no evidence to back up these claims.
• BEST ALKALINE WATER MACHINE – click here
WHAT IS FILTERED WATER?
Filtered water is water that has been treated by passing it through a water filtration device to remove contaminants.

Bottled mineral water and most tap water supplies are filtered to remove harmful contaminants to make the water safe to drink and taste better.
To find out if you’re home water supply has been filtered and is safe to drink you should contact your local water provider.
TYPES OF FILTERED WATER
When covering – what’s the difference between alkaline water and filtered water – we need to take a look at the different types of filtered water. There are many types of water filtration technologies but the aim of every one of them is the same – to remove contaminants from the water.

Water filtration is used to make water taste better, look better, and safe to drink. Without water filtration, we would all be drinking dirty water. The four main types of water filters used in the domestic setting are activated carbon filter, reverse osmosis, ion-exchange, and distillation.
Activated Carbon Filter
An activated carbon filter is the most common type of water filter. It is regularly used in domestic water filtration devices. It uses an ‘activated-carbon’ medium to bind contaminants as the water passes through the filter.
The contaminants are trapped inside the carbon medium while the water is free to pass through. Carbon filters are effective in removing the taste of chlorine, other chemicals, and a wide range of contaminants in your drinking water.
Ion Exchange
An ion-exchange water filter removes contaminants from water in the form of undesirable dissolved ions by replacing them with harmless ions of the same electrical charge from using an ion-exchange resin.
An ion exchange filter is inexpensive and effective for the removal of dissolved inorganics contaminants such as arsenic, fluoride, nitrates, uranium, and sulfates. They are also regenerable for continuous usage.
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis is an incredibly effective way of filtering water. The process removes up to 99% of all water contaminants to produce high-quality clean water.
Reverse osmosis filtration passes water through a semi-permeable membrane with a pore size so small – it allows water molecules to pass but blocks microscopic contaminants.
The pore size of a reverse osmosis filter membrane can be as small as 0.0001 microns. These membranes greatly reduce the presence of harmful metals, lead, mercury, and microbes.
Distillation
A distillation filtration system boils source water into steam before condensing it back into water. As water is transformed to steam it leaves behind its contaminants.
It then travels through the distillation apparatus in its gaseous form before being cooled to condense back into water. The filtered cooled water is then collected in a reservoir.
READ NEXT
COFFEE & ALKALINE WATER – click here
HOW TO TEST WATER HARDNESS AT HOME – click here
WHAT IS TDS IN WATER? – click here
HOW TO USE A PH TEST STRIP – click here
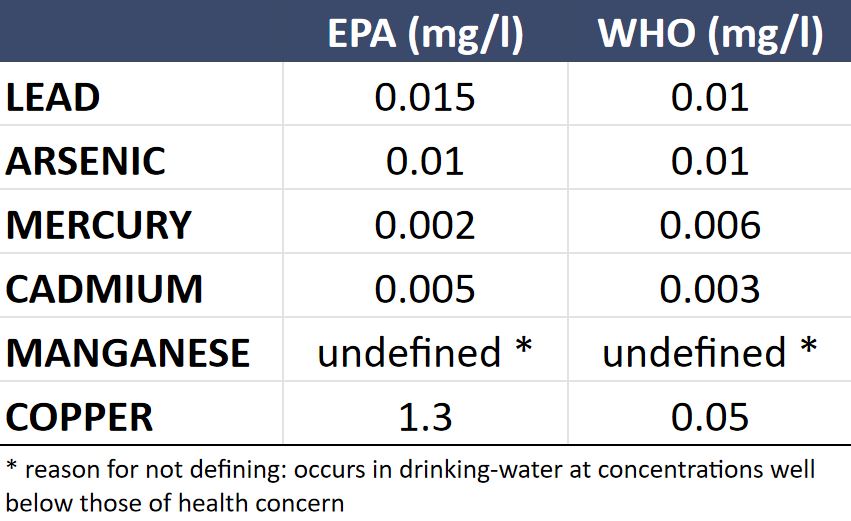
CONTAMINANTS IN DRINKING WATER
What are the most common contaminants found in drinking water? According to the United States Environmental Protection Agency there are five types of contaminants in our drinking water: physical, chemical, biological, and radiological.

Physical – sediment suspended in the water of lakes, rivers, and streams. Often caused by soil erosion.
Chemical – nitrogen, bleach, pesticides, metals, and toxins produced by bacteria, human or animal drugs.
Biological – organisms such as microbes and viruses. Often referred to as microbiological contaminants they include bacteria, viruses, parasites, and protozoa.
Radiological – radiological contaminants are hazardous unstable atoms that emit hazardous ionizing radiation. Cesium, uranium, and plutonium are examples of radiological contaminants. You definitely don’t want these in your drinking water.

IS ALKALINE WATER BETTER THAN FILTERED WATER?
Alkaline water and filtered water are two completely different types of water. Alkaline water is better if you want high pH water with higher than normal alkalinity.
Filtered water is better if you want clean, purified water. It has been passed through a water filtration system to remove contaminants. Water filtration purifies water to remove harmful substances and make it safe for drinking.
IS ALKALINE WATER JUST FILTERED WATER?
No, alkaline water is not just filtered water. Alkaline water is a special type of water that has an increased level of alkalinity. It is the opposite of acidic water.
Alkaline water has a pH above 7. Some people drink it for its potential health benefits – but there is no evidence to back up these health claims.
RELATED
HEAVY METALS IN DRINKING WATER – click here
WATER SOFTENER vs WATER FILTER – click here
ARE THERE MINERALS IN WATER? – click here
PROS & CONS OF REVERSE OSMOSIS WATER – click here

ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Water Filtration Specialist
Sam joined the Pure Water Ions team in the fall of 2021. He is a graduate of the University of Oregon where he qualified with a BSc in Earth Sciences. He has over 10 years of experience in the water filtration industry and specializes in multi-stage water filtration devices.
Sam likes to spend his time hiking, fishing, and exploring the great outdoors. When he’s not writing about the latest water filtration technologies he likes to explore Marys Peak in Benton County with his trusty Ford Bronco and German Sheperd Max.
[e] sam.kemper@purewaterions.com
[t] 503-232-4012 ext. 103
[a] S. Kemper, PWI, 2170D SE 8th Ave, Portland, OR 97214, USA